
2 days ago · Traditional literature review / narrative review: Characteristics: Describes and appraises previous work but does not describe specific methods by which the reviewed studies were identified, selected and evaluated; Uses: Overviews, discussions, critiques of previous work and the current gaps in knowledge; Often used as rationale for new researchAuthor: Stephanie Roth · Editorial review is an assessment of an article undertaken by a member of the editorial staff. For some sections of the journal, editorial review may be the only assessment taken of an article. This is more often the case for non-research articles such as book reviews, commentary, opinion etc.(although in some journals these sections are peer-reviewed as well).Author: Jessica Lange · A manual review may not be necessary. Require a team. Generally, two or more individuals independently review each article separately to determine whether it meets inclusion criteria. Conflicts are solved by a third party. Can be completed by individuals. Results do not need to be reviewed for inclusion or exclusion by multiple individuals. Protocol-driven
Western University
A systematic review attempts to collate all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a specific research question.
Research librarians can partner with current Duke Health faculty, staff, different types of review articles, and students on systematic reviews. Add us to your author team and we will design different types of review articles manage complex, thorough searches in multiple databases.
We will also provide you with:. Time : On average, systematic reviews require 18 months of preparation. A team: A systematic review can't be done alone! You need to work with subject experts to clarify issues related to the topic; librarians to develop comprehensive search strategies and identify appropriate databases; reviewers to screen abstracts and read the full text; a statistician who can assist with data analysis if you are doing a meta-analysis ; and a project leader to coordinate and write the final report.
A clearly defined question : Clarify the key question s of you systematic review and the rationale for each question. Use the PICO framework to identify key concepts of the question. A written protocol : You need to write a protocol outlining the study methodology.
Need help writing a protocol? See the University of Warwick's protocol template. A registered protocol : After you write the protocol, you should register it with a review registry. There are different types of review articles review registries available, such as PROSPERO or OSF. Registration is free and open to anyone undertaking systematic reviews.
Some journals also publish systematic review protocols. Comprehensive literature searches : First, identify systematic reviews that may address your key questions. Then, identify appropriate databases and conduct comprehensive and detailed literature searches that can be documented and duplicated.
Citation management: You should have working knowledge of EndNote to help manage citations retrieved from literature searches. Follow reporting guidelines : Use appropriate guidelines for reporting your review for publication. For more information about the nuances of conducting systematic reviews, contact your Medical Center Librarian! medical-librarian duke. edu Library staff, services, and resources are available online. Librarians are available remotely Building access is restricted.
It looks like you're using Internet Explorer 11 or older. This website works best with modern browsers such as the latest versions of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. If you continue with this browser, you may see unexpected results.
Duke NetID Login Building Access: Restricted Library Hours. Books Journals Mobile Apps Report an Access Issue. Tool Sets For Biostatistics Clinicians Educators Global Health MBS Program Medical Students MMCi Program Nursing Path Asst Program Physical Therapy PA Program Researchers Community Partners. Using Databases CINAHL Embase JCR Impact Factors Different types of review articles Micromedex Ovid MEDLINE PubMed Scopus Web of Science.
Meet a Librarian Request a Consultation Find Your Liaisons. Classes Register for a Class Request a Class Self-Paced Learning. Search Assistance Literature Search Systematic Review Animal Alternatives IACUC. Research Impact Publication Metrics Research Impact Request Where Duke Publishes. Citation Mgmt Software Overview EndNote Mendeley RefWorks Sciwheel Zotero. Directions and Maps Floor Plans Reserve a Seat Reserve a Locker Blog Newsletter Annual Snapshot, different types of review articles.
Library LibGuides Systematic Reviews: the process Home Search this Guide Search. Systematic Reviews: the process: Home. What is a Systematic Review?
How can the Library help? To get started: review our policies look over and complete our literature search planning form email us to set up a consultation attach the planning form to the email, different types of review articles.
What does it take to do a systematic review? Contact the Medical Library JavaScript disabled or chat unavailable. Duke Health Duke University Duke Libraries Medical Center Archives Duke Directory.
Seeley G. Mudd Building 10 Searle Drive medical-librarian duke. edu
Types of Reviews
, time: 8:25Types of Article Reviews: Formats and Tips on Writing - blogger.com
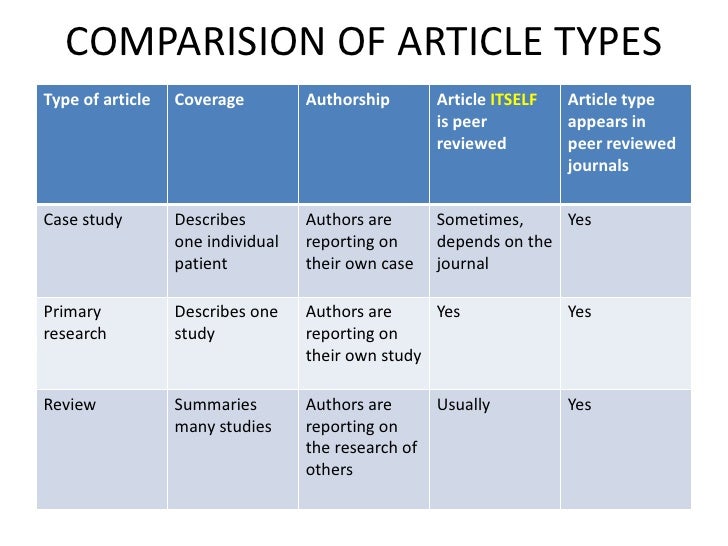
· Editorial review is an assessment of an article undertaken by a member of the editorial staff. For some sections of the journal, editorial review may be the only assessment taken of an article. This is more often the case for non-research articles such as book reviews, commentary, opinion etc.(although in some journals these sections are peer-reviewed as well).Author: Jessica Lange · A manual review may not be necessary. Require a team. Generally, two or more individuals independently review each article separately to determine whether it meets inclusion criteria. Conflicts are solved by a third party. Can be completed by individuals. Results do not need to be reviewed for inclusion or exclusion by multiple individuals. Protocol-driven 2 days ago · Traditional literature review / narrative review: Characteristics: Describes and appraises previous work but does not describe specific methods by which the reviewed studies were identified, selected and evaluated; Uses: Overviews, discussions, critiques of previous work and the current gaps in knowledge; Often used as rationale for new researchAuthor: Stephanie Roth

No comments:
Post a Comment